The FAO of the UN predicts that the world’s population will reach 9.8 billion by 2050, and the demand for food is set to increase by 50%, and demand for animal-based foods by nearly 70%. Fish, including farmed salmon, can offer a solution to meeting this increased demand. As demand increases there will be increased pressure on the already over-exploited wild fish reserves, which is why farmed fish is required to efficiently manage and maintain both wild fish stocks and the ocean’s natural biodiversity.
A constantly evolving world
Over the past few years every industry has been experiencing rapid, extensive, and sometimes devastating change and the food industry is no exception.
Our world is shifting, populations are growing, our climate is changing, and there is more pressure than ever on our food systems. The demand for food is set to increase by 50%, and demand for animal-based foods by nearly 70%.
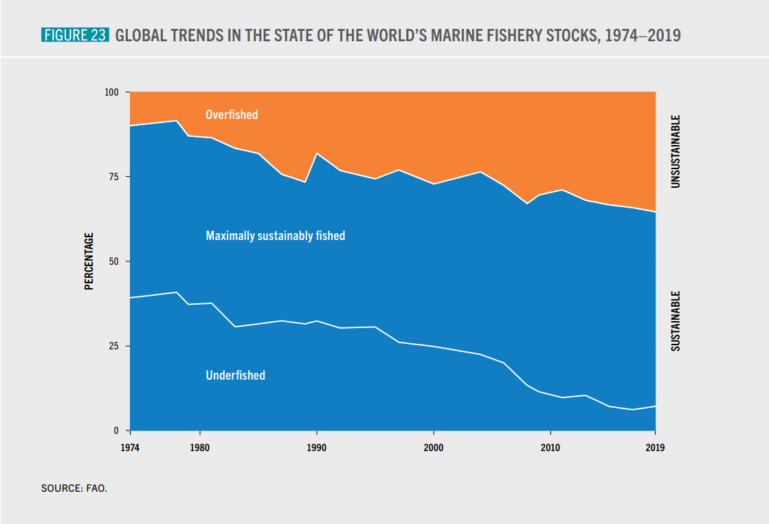
Source: FAO, Global trends in the state of the world's marine fish stocks, 1974-2019.
Since 1961 the annual global growth in fish consumption has been twice as high as population growth, demonstrating that the fisheries and aquaculture sector is crucial in meeting FAO’s goal of a world without hunger and malnutritionJosé Graziano da Silva, FAO Director-General
Introducing aquaculture
- Aquaculture is the farming of fish, shellfish, or mollusks in water
- It is one of the most eco-efficient forms of protein production
- About 50% of seafood eaten worldwide comes from aquaculture
- It is the fastest-growing global production sector
- In 2019, the fraction of fish stocks sustainably fished decreased to 64.6%
- The planet is 70% ocean, which means that if aquaculture is performed correctly, the oceans can offer significant contribution to sustainable food systems
We must plant the sea and herd its animals using the sea as farmers instead of hunters. That is what civilization is all about - farming replacing huntingJaques-Yves Cousteau, Oceanographer
What is salmon farming?
Just like we farm animals on land, aquaculture is the farming of fish in the ocean. Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae (e.g. Atlantic salmon, Pacific salmon).

Two salmon farmers inspecting fish in a salmon farm
Salmon fish farming started on an experimental level in the 1960s, but became an industry in Norway in the 1980s, and in Chile in the 1990s. The farmed salmon industry has grown substantially in the past 40 years, and today approximately 70% of salmon produced worldwide is farmed. In 2015 more than 2,200,000 tons of farmed salmon were produced, while in comparison around 880,000 tons of wild salmon were caught.
Atlantic salmon farming has traditionally been dominated by a small number of farming regions – Chile, Norway, Canada, and Scotland – as several natural conditions often have to be present to ensure optimal salmon farming production. Such conditions include: cold water temperatures varying between 8°C and 14°C (46°F – 57°F), a sheltered coastline, and optimal biological conditions. Today, salmon farming is also taking place in Australia, Faroe Islands, Iceland, Ireland, and New Zealand.
The salmon farming production cycle lasts about 3 years. The first year of production takes place in controlled freshwater environments, and then the farmed salmon are transported to seawater cages. Once the farmed salmon reach a harvestable size, they are transported to processing plants to be prepared for sale. For consumers, most farmed salmon is sold as salmon fillets, although you can also purchase whole fish.
Fish farming holds tremendous promise in responding to surging demand for food which is taking place due to global population growth.State of World Fisheries Report, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
Responsibly farmed salmon supports global food system solutions by:
- Contributing a nutrient-rich food source to diets that meets global dietary recommendations
- Delivering high-quality and eco-efficient protein to help meet growing global demand
- Driving continuous innovations that help support healthier diets and more resilient global food systems
- Providing a food source that is celebrated in cuisines and communities around the world
The future of salmon farming
We recognize that an increased production of farmed salmon is required to ensure future demands for protein are met, however this must be matched by significant reductions in environmental impact and improvements in resource efficiency. We recognize our ability – and our responsibility – to drive positive change at scale, and we are committed to seeking and supporting advancements in aquaculture that drive healthy, sustainable food systems.
Responsible aquaculture methods can help ensure the protein we eat is produced in a way that supports nutritious diets and more sustainable food systems.







Follow us on social media and sign up for the newsletter
X
Threads
LinkedIn
Instagram
YouTube
Newsletter